This is where the transformative power of AI and automation in UX design comes into play. By strategically integrating these cutting-edge technologies, businesses can streamline workflows, accelerate insights, and deliver superior user experiences that drive tangible business outcomes. This intelligent approach to experience design promises unprecedented value, redefining how we connect with users and employees alike.
Addressing Business Bottlenecks
The traditional UX design process, while foundational, frequently holds some bottlenecks for modern businesses. From extensive research and user testing to iterative prototyping and development hand-offs, the sheer manual effort involved can be substantial. This often leads to extended time-to-market for new features or products, inflated operational costs, and the critical risk of falling behind competitors who are quicker to adapt and innovate.
Consider the common pain points experienced across various sectors. Organizations often navigate intricate digital ecosystems, from platforms handling complex financial transactions to systems managing vast logistical networks or critical healthcare operations. The need for intuitive, secure, and personalized digital interactions is paramount. Intricate user journeys on transactional platforms, for instance, frequently lead to high abandonment rates and lost revenue. Similarly, user interfaces for sophisticated operational systems — be it for complex machinery, patient data management, or intricate supply chain logistics — demand absolute clarity, precision, and ease of use to ensure safety and efficient operations. In environments rich with data, advanced digital operations necessitate seamless human-system interaction, where complex information must be presented in an understandable and actionable format; poor UX here can lead to costly errors, inefficiencies, and even significant safety concerns.
For executive leadership, the message is clear across all functions: optimizing the UX design process is no longer optional. It’s a strategic necessity to maintain a competitive edge and drive digital transformation. The lengthy, complicated, and repetitive nature of current processes represents a significant drain on resources and a tangible barrier to achieving strategic goals. The struggle to kickstart projects and maintain momentum through iterative cycles is a widely felt pain point, impacting project timelines and overall business agility.
Solutions to Common Problems
AI and automation aren’t here to replace human creativity; rather, they augment it, allowing UX professionals to shed tedious tasks and focus on higher-value, strategic thinking. These technologies are fundamentally reshaping the UX landscape in several powerful ways, offering direct and impactful solutions to the bottlenecks many businesses face.
These intelligent tools can accelerate research and insights, directly tackling the time-consuming nature of early-stage UX. AI algorithms can rapidly process vast amounts of qualitative and quantitative data from user surveys, interviews, analytics, and social media. This capability allows for faster identification of patterns, pain points, and user needs, leading to more data-driven design decisions. Automated user testing tools, often powered by AI, streamline everything from recruiting participants to analyzing their interactions and identifying usability issues, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with gathering feedback. Furthermore, AI can predict user behavior based on historical data, allowing designers to proactively address potential usability challenges and optimize user flows before development even begins, shifting from reactive problem-solving to proactive design.
In terms of streamlining design and prototyping, AI offers a robust solution to the manual iteration burden. AI can assist in generating design variations based on predefined parameters and user data, offering designers a wider range of options to explore and iterate upon rapidly. Automated prototyping tools can create interactive prototypes directly from wireframes or design specifications, accelerating the visualization of user journeys and interaction flows. AI also plays a crucial role in design system management, helping maintain consistency across digital products by automatically flagging deviations or suggesting components that adhere to established guidelines, thus reducing design debt and inconsistencies across large design portfolios.
AI and automation also significantly enhance personalization and adaptability, directly addressing the escalating demand for tailored user experiences. AI can enable interfaces to adapt in real-time based on individual user preferences, behavior, and context, delivering highly personalized experiences that resonate more deeply. Moreover, AI can analyze content performance and suggest optimizations for text, images, and multimedia to improve engagement and relevance for specific user segments, leading to more effective digital communication.
Finally, these technologies are crucial for improving development hand-off and iteration, a common friction point in many projects that slows down delivery. For certain UI components, AI can generate basic code snippets directly from design files, reducing manual coding effort and potential errors during development hand-off. AI can also manage and analyze the results of A/B tests more efficiently, providing rapid insights into which design variations perform best and automatically implementing the winning designs. By establishing continuous feedback loops between user data, design, and development, automation enables faster iterations and continuous improvement of digital products, moving away from rigid, linear processes that often delay critical updates.
Tangible Benefits
The integration of AI and automation in UX design translates directly into significant business advantages, offering concrete solutions to core business objectives and addressing the common pain points that erode profitability and efficiency.
This strategic shift directly leads to increased revenue. Intuitive and personalized experiences result in higher user satisfaction, increased engagement, and improved customer loyalty, which in turn drives repeat business and subscriptions. Streamlined user journeys and optimized interfaces reduce friction points, leading to improved conversion rates for sales, sign-ups, and other key business objectives. By significantly accelerating the design process, new features and products can be launched quicker, allowing businesses to capitalize on market opportunities ahead of competitors.
Organizations also benefit profoundly from reduced costs. The automation of repetitive, time-consuming tasks frees up valuable UX design and development resources, allowing them to focus on more strategic and complex challenges. Data-driven insights and automated validation reduce the likelihood of costly design flaws and extensive reworks during the development phase. Overall, streamlined workflows and automated processes lead to greater operational efficiency and long-term cost savings, directly addressing the financial strain of manual and error-prone processes.
Finally, AI and automation contribute significantly to lowered risks. Early identification and resolution of usability issues through AI-powered testing and analysis reduce the risk of launching products with poor user experiences that could harm brand reputation and result in costly redesigns or even regulatory non-compliance. Automation can also assist in ensuring designs adhere to stringent compliance standards and accessibility guidelines, thereby mitigating legal and reputational risks. Furthermore, AI-driven insights provide a more robust basis for design decisions, minimizing the risk of making choices based on assumptions or incomplete data, a common source of project failure and unforeseen expenditures.
An AI-Powered Framework for Innovation
To fully harness the power of AI and automation, it’s essential to understand how these technologies integrate into a modern, iterative UX design framework. This structured approach ensures that every step, from initial concept to continuous optimization, is enhanced for efficiency, insight, and user value.
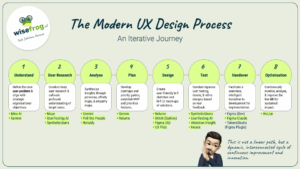
1. Understand: Defining the Challenge & Objectives
This foundational step involves clearly defining the core user problem and meticulously aligning design solutions with overarching strategic organizational goals.
AI-powered visual collaboration platforms (e.g., Miro with Miro Assist): These tools facilitate collaborative problem mapping, identifying user pain points and operational friction across diverse teams. They offer AI-powered layout improvements, automated idea clustering, and intelligent summaries of discussions, significantly reducing manual effort and accelerating insight. For example, in a virtual workshop, AI can instantly identify a recurring “documentation error” theme linked to a specific region, highlighting a key problem that directly impacts user experience and operational efficiency.
Advanced AI models for text generation and understanding (e.g., Gemini, ChatGPT): These models rapidly synthesize key challenges and emerging trends from vast unstructured data, defining problems from a holistic user perspective. By feeding them customer feedback logs, internal reports, or market analyses, they can identify themes, pain points, or generate refined problem statements. This accelerates problem definition and reduces costs in manual data review, ensuring clear, concise organizational objectives that reflect true user value. For instance, an AI can quickly identify top recurring user pain points from customer support transcripts, suggesting a refined problem statement for a UX initiative.
2. Research: Uncovering User Needs & Behaviors
This phase involves conducting deep user research to cultivate a profound understanding of target users, their varied needs, pain points, and behaviors within complex digital environments. The challenge lies in researching incredibly diverse user groups, from individual consumers to large enterprises and internal employees.
AI-powered user testing platforms (e.g., Maze): These platforms enable rapid, unmoderated testing of digital touchpoints with a diverse panel of real users globally. They provide automated analysis of test results, heatmaps, path analysis, and sentiment analysis of user comments, offering insights into user behavior and reducing research time and costs. They also identify friction points that could lead to abandoned transactions, lowering the risk of lost conversions. For example, AI heatmaps can immediately highlight confusion around specific input fields in a checkout flow, preventing potential customer drop-offs.
AI-powered human insight platforms (e.g., UserTesting AI): These tools provide deeper qualitative insights into complex user journeys through video recordings of real users. They offer AI-powered analysis of video recordings and transcripts, automated highlight reels of key moments (user confusion, delight), and smart tagging of themes, which significantly reduces analysis time and costs. This leads to more intuitive designs, increasing user adoption and revenue. A short, AI-generated highlight reel can clearly demonstrate a usability barrier for a key user segment struggling with a new feature.
Synthetic user generation (e.g., SyntheticUsers): These tools generate simulated user behavior and feedback for rapid, early insights without the need for immediate real user recruitment. By defining personas and scenarios, automated tests can explore user edge cases or early concepts, providing realistic user paths and AI-generated qualitative feedback. This accelerates early research, reduces initial testing costs, and identifies potential usability issues before live testing.
3. Analyze: Synthesizing Insights into Actionable Frameworks
This crucial step focuses on making sense of vast amounts of research data from diverse sources—customer feedback, operational logs, market trends—to create clear, actionable insights that drive strategic design decisions, ensuring all efforts are data-driven and user-centric.
Advanced AI models for text generation and understanding (e.g., Gemini, ChatGPT): These models synthesize qualitative data from various sources to identify themes and populate analysis frameworks. By feeding them interview transcripts, survey responses, or open-ended feedback, they can identify themes, extract quotes, or suggest categories. This reduces costs in manual analysis and provides detailed user persona descriptions or populated empathy map sections, lowering the risk of misinterpreting user needs. For instance, AI can generate a summary of key user pain points from raw interview notes and suggest categories for an affinity map.
AI-powered survey and feedback analysis (e.g., Poll the People): These tools rapidly gather quantitative and qualitative feedback on specific design concepts or user preferences from a broad audience. They offer AI-driven analysis of open-ended survey responses, sentiment analysis, and automatic categorization of feedback, accelerating insight and reducing costs. This validates assumptions and prioritizes features based on user sentiment, supporting revenue increase and lowering the risk of building unwanted features.
AI-driven qualitative data analysis platforms (e.g., Notably): These platforms streamline the analysis of qualitative data, quickly clustering observations and generating concise summaries. By inputting research notes, AI features can group and summarize findings, identifying emergent themes. This reduces costs in manual analysis and builds robust insights for designs that improve efficiency and reduce risks for users.
4. Plan: Developing Structure & Prioritization
This phase translates high-level problem definitions and user insights into concrete structural plans. This includes defining information architecture for complex systems, guiding content hierarchy, establishing minimum viable products (MVPs), and prioritizing features for development, ensuring a clear roadmap that delivers user value efficiently.
Advanced AI models for planning and strategic guidance (e.g., Gemini, ChatGPT): These models assist in generating initial sitemap structures and brainstorming features that reflect user mental models and deliver user value. By providing problem statements and user insights, they can suggest diverse sitemap structures, comprehensive lists of MVP features, or prioritization frameworks. This accelerates planning, reduces costs, and identifies potential structural issues that might confuse users, lowering the risk of poor user adoption.
AI-powered website builders with sitemap generation (e.g., Relume (Sitemap)): These tools rapidly generate website structures and sitemaps, ensuring a logical flow for users and content. By inputting content themes or user flows, AI features can visualize information architecture and hierarchy, speeding up planning and reducing costs. This visual representation of content hierarchy lowers the risk of poor navigation and improves user experience.
5. Design: Creating Solutions from Sketch to High-Fidelity
This iterative phase transforms planned structures into tangible, interactive design solutions, ranging from rough low-fidelity sketches for quick concept validation to pixel-perfect high-fidelity UI mock-ups ready for development.
AI-powered wireframe generation (e.g., Relume Wireframe): These tools rapidly create low-fidelity wireframes, quickly visualizing user flows and structural concepts. They speed up concepting and reduce costs, while lowering risk by allowing early validation of user flows.
AI-powered design system management (e.g., Relume Style Guide): These tools ensure consistent application of brand guidelines and design system elements across high-fidelity UI, building user trust through a predictable interface. They ensure consistent high-fidelity UI mock-ups and adherence to established brand guidelines, reducing costs in rework and lowering the risk of brand inconsistency.
AI-powered design suggestion (e.g., Stitch (Galileo)): These tools generate complex, high-fidelity UI screens directly from text prompts, accelerating design exploration. They efficiently produce concepts and reduce costs, allowing faster exploration of design options for improved user flows and increased user engagement.
Core design tools with integrated AI capabilities (e.g., Figma (AI)): These platforms serve as a central hub for collaborative design, enhanced by AI for efficiency. They offer AI-generated initial high-fidelity layouts, assistance with content generation, image manipulation, and design system adherence.
AI-powered wireframing and design suggestions (e.g., UX Pilot): These tools offer AI-driven wireframing and design suggestions, accelerating the initial design phase and ensuring user-centric layouts.
6. Prototype Test: Validating & Iterating Solutions
This critical step involves conducting rigorous user testing on interactive prototypes of new or redesigned digital products to gather feedback, identify usability issues, and iterate rapidly before costly development. The goal is to ensure the user experience is flawless and truly meets user expectations.
Core tools for interactive prototyping (e.g., Figma): These tools allow the creation of highly interactive and realistic mock-ups for authentic user behavior data during testing. Future AI capabilities may assist in generating complex interactions or identifying potential usability issues within the prototype itself.
Synthetic user generation for testing (e.g., SyntheticUsers): These tools provide rapid, scalable feedback on prototypes by simulating user behavior without needing real users for every iteration. They dramatically reduce costs and time in early testing, quickly highlighting design flaws and lowering risk before engaging real users. For example, AI can highlight a specific step where synthetic users consistently fail to complete a task in a simulated test.
AI-powered human insight platforms (e.g., UserTesting AI): These tools gather deep qualitative insights from real users interacting with prototypes, accelerating the analysis of their thoughts and emotions.
AI-powered visual attention prediction (e.g., Attention Insight): These tools predict where users will look on a design, optimizing visual hierarchy before live testing. They provide instant feedback on visual effectiveness and reduce costs by optimizing designs pre-test, ensuring critical elements are seen.
AI-powered heuristic evaluation (e.g., Heurix): These tools automate heuristic evaluations to quickly identify potential usability issues based on established UX principles. They automate a time-consuming manual process and provide actionable recommendations for improvement.
7. Handover to Development & Implementation Assistance
This phase ensures a seamless transition of complex UI designs from design to engineering, maintaining design fidelity and providing clear, actionable specifications for development teams. This is where design integrity meets execution efficiency, ultimately delivering the intended user experience as designed.
Core design tools for developer handoff (e.g., Figma (Dev Mode), Figma-Claude integration): These tools provide developers with inspectable design files and code snippets directly within the design environment, ensuring accurate implementation. They streamline communication and reduce development time costs. AI enhancements can predict developer needs and flag complexities, lowering the risk of misinterpretation.
Design token management for code synchronization (e.g., Tokens Studio (Figma Plug-in)): Although not native AI, these tools maintain a consistent design system across all digital products, ensuring brand adherence and technical scalability. They significantly reduce costs in manual updates and maintenance by synchronizing design decisions directly into code formats, lowering the risk of design inconsistencies and technical debt.
8. Optimization: Continuous Improvement of Live Solutions
This final, ongoing phase involves monitoring the performance of live digital products, analyzing real-world user behavior, and continuously iterating to improve efficiency, satisfaction, and business outcomes. This is the crucial feedback loop that ensures sustained value and a constantly evolving positive user experience.
Behavior analytics & feedback with AI insights (e.g., Hotjar): These tools gather visual insights into how users interact with live products, identifying drop-off points and struggles. They provide heatmaps, session recordings, automated summarization of user feedback, and intelligent flagging of unusual user behavior, reducing costs in manual analysis. This directly impacts conversion rates and user satisfaction, supporting revenue increase and lowering the risk of negative customer sentiment.
This strategic adoption of AI and automation offers a clear path to overcoming the current bottlenecks in UX design. It’s an opportunity to embrace a more efficient, innovative, and impactful approach to creating digital experiences.
Download PDF: AI-Powered UX workflow – Wisefrog

